- MathNotebook
- MathConcepts
- StudyMath
- Geometry
- Logic
- Bott periodicity
- CategoryTheory
- FieldWithOneElement
- MathDiscovery
- Math Connections
Epistemology
- m a t h 4 w i s d o m - g m a i l
- +370 607 27 665
- My work is in the Public Domain for all to share freely.
- 读物 书 影片 维基百科
Introduction E9F5FC
Questions FFFFC0
Software
Analyze the 99 concepts discussed in the Math Companion and figure out their building blocks.
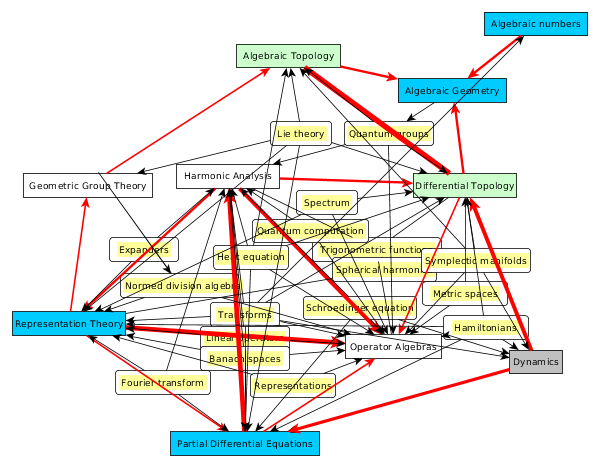
基本概念
- Orientation: Marked and unmarked opposites, outside and inside, antisymmetry, sign of permutation.
- Amounts: Summation. Identifying units (items, objects, areas, etc.) with numbers and adding them up.
- Smoothness: Change in one dimension is (extrinsically) comparable to (or even, intrinsically, of a much smaller order than) change in another dimension. Compare with difference between subconscious continuum and conscious discreteness.
- Generating functions relate: symmetry of analytic functions, algorithms, finite combinatorial symmetry. (Think of as a vector bundle - the infinite sequence ({$x_i$}) is the base space, and the coefficient is the fiber, and the fibers are related.)
- Linear operators - something you can have more of or less of (proportionately) - transformational action (like rotation or translation).
Math Companion Concepts
I am trying to organize the 99 concepts below. Next to each concept I have assigned the branches of math where they are important, with the 26 branches taken from the same Companion, and referenced by the numbers given in the book, as follows:
Axioms
22., 23. Zermelo-Fraenkel Axioms. Ways of constructing sets; of knowing if they are the same set; and of assuring that they don't have cycles.
22. Axiom of Choice. Given a set, you can select a representative element.
22. Axiom of Determinacy. The existence of a winning strategy for at least one of two players of an infinite game.
23., 22. Peano Axioms. Describes the natural numbers.
- Natural numbers
Numbers
11., 6., 26., 4. Pi
1., 22. Irrational and Transcendental Numbers
- Solutions and nonsolutions to linear equations, polynomials equations, with integer coefficients.
Functions and mappings
9. Determinants. Sum of oriented permutations = oriented volume of matrix.
18., 6., 17., 10a., 10b., B1. Knot Polynomials
18b., 18a. Generating Functions
2., 11. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
X 11., 7., 15. Trigonometric Functions
XX 11., 9., 15., 7. Spherical Harmonics
12., 11., 21. Linear and Nonlinear Waves and Solitons
2. Gamma Function
2., 5. L-Functions
2., 5., 7. Riemann Zeta Function
22., 15., 25. Measures
1., 4., 6., 15. Quadratic Forms
12. Distributions
19 b., 22., 11., 26. Probability Distributions
7., 4., BX1. Differential Forms and Integration
X 9., 15., 23. Tensor Products
XXX 9., 15., 11., 12. Linear Operators and Their Properties
4. Modular Forms
6., 7., 10a., 1. Universal Covers. A space Y and a continuous surjection from Y to X.
6., 7. Vector Bundles. A space E and a continuous map p from E to X such that the inverse image {$p^{-1}(x)$} is an (n-dimensional) vector space.
25. Ising Model
Equations
12. Euler and Navier-Stokes Equations
XX 12., 11., 15., 7., 6. Heat Equation
XX 12., 14., 15., 24., 25., 11. Schroedinger Equation
12., 18., 21., 11., 19b. Special Functions
4. Elliptic Curves
Identifications
XX 11., 9., 12., 26. Fourier Transform
- Use complex roots {$e^{ir\theta}$} as set of frequencies to identify sequence and function.
11. Fast Fourier Transform
XXX 11., 15., 12., 19b., 18., 7., 2., 14., 9. Transforms
- Identifies sequence (and its self-symmetry) and function (and its self-symmetry).
Objects - Structures
22. Countable and Uncountable Sets
14. Mandelbrot
22. Ordinals
22. Cardinals
23., 6. Categories
19a. Graphs
X 18., 20., 11., 9. Expanders
10a. Buildings
10a., 9. Leech Lattice
4., 5. Varieties
20., 9., 18. Matroids
3., 10b. Modular Arithmetic
10a., 12., 6. Fuchsian Groups
X 5., 4., 15., 7., 6., 11., 23. Quantum Groups
- Algebras of polynomials up to equivalence on a variety - where the points are group elements.
- Map from X to Y gives rise to adjoint map from C[Y] to C[X].
- Algebras has coproduct. Group structure yields Hopf algebra or quantum group (which has additional structure analogous to that of a Lie group).
- Makes sense over any field.
- There exist noncommutative Hopf algebras based on deformations q, thus grounding noncommutative geometry.
- Hopf algebras are the next simplest categories after abelian groups that admit a Fourier transform.
- Axioms of Hopf algebra are symmetric under arrow reversal.
- Bicrossproduct quantum groups are simultaneously coordinate algebras and symmetry algebras.
1. Galois Groups
6., 4. Braid Groups
1. Ideal Class Group
10b., 9., 17. Monster Group
10b., 9., 19b. Permutation Groups
1., 4., 9. Rings, Ideals, and Modules
4., 1., 5. Schemes
1. Number Fields
X 9., 15. Representations
X 9., 15., 10a. Quaternions, Octonions and Normed Division Algebras
23., 22. Models of Set Theory
Spaces
4., 6. Projective Space
7., 6., 4., 8. Manifolds
7., 4., 16. Calabi-Yau Manifolds
X 7., 22., 18., 20., 13., 15. Metric Spaces
7., 6., 11., 10a. Riemann Surfaces
X 7., 6., 15., 14., 24. Symplectic Manifolds
4., 7., 16. Orbifolds
15. C*-Algebras
15. Function Spaces
15., 11. Hilbert Spaces
6., 7., 4. Topological Spaces
8., 6., 7., 4., 1., 11. Moduli Spaces
XX 15., 12., 11., 9. Normed Spaces and Banach Spaces
15. Von Neumann Algebras
Properties and invariants
7., 14. Dimension
13., 7. Curvature
7. Compactness and Compactification
6., 7., 4. Genus
XX 14., 12., 15., 9., 17., 16., 7. Hamiltonians
X 15., 9., 7. Spectrum
9., 10 b. Jordan Normal Form
14., 12. Dynamical Systems and Chaos
25. Phase Transitions
Algorithms
2. Euclidean Algorithm and Continued Fractions
14., 7., 12., 11., 24. Variational Methods
X 20., 11., 15., 19b., 26. Quantum Computation
20., 9., 14., 10a., 18. Simplex Algorithm
21., 11. Wavelets
20. Computational Complexity Classes
7., 6., 12. Ricci Flow. Replaces a manifold with a smoother manifold.
14., 12., 7. Optimization and Lagrange Multipliers
High level concepts
10a., 4., 6., 16. Duality
1., 2., 4. Local and Global in Number Theory
Theories
X 9., 6., 10a., 10b., 12., 17., 7. Lie Theory
6. Homology and Cohomology
6., 15. K-Theory
